It’s been a while since I last posted…
There is always a reason for that. My reason was a sum of many different variables. Just as the great mentor said, luck is the sum of many coincidences, that’s what happened in my case as well.
Where do I begin?
Jobwise: Capital controls, working day and night, a lot to do and no time to do it…
Blogwise: I had a very strange setup with my blog (and a very very outdated one I might add). Since I am using Heroku, they decided to change their stack and migrate from Cedar 10 to Cedar 14 . Ok I said what the hell lets do it.
Alas, I had a serious problem with libssl0.98 which was built inside my php module and was not supported in Cedar 14. (whoever wants to do the upgrade have a look here first).
Long story short I fixed it, and I also found that many posts I did with various hacks for the pg4wp plugin were incorporated into a single release from kevinoid : here
I will contribute also into some changes that have to be taken into account since the module is quite old and I have previously stated that it’s not at all well written.
That’s not the main point of this post though.
I wanted to share an experience I keep coming across lately.
Now according to popular trends we are experiencing (and will experience in the future) a huge bloom of the microserviced architecture. This guy here explains how and why they decided to go for the microserviced architecture.
I agree. There are many benefits when having a monolithic single (and obsolete at times) repo for web applications. It is a nice solution when your company is scaling, and you have to maintain a lot of different parts. Especially if you have different teams and each team wants to “do their own thing” about a solution.
However it’s not the solution to Everything!
I will elaborate more:
I recently had to debug an http step based procedure (client requests this page, books this ticket, goes there, etc.) that was using 3 different instances of different technologies over http. The one was python and wsgi, the second was php with apache and the third one was ruby with unicorn.
Try to debug this. I dare you. Seriously. I had in my local setup all 3 different instances running with 3 different IDE’s and all running their debugger. Ok, ok you say that Docker will simplify the installation. I agree it does, but it does not help the debugging at all.
The most important thing though isn’t the debug/testing of many different apps over http.
It’s the HTTP by itself.
And believe me, I have seen a lot of “Senior” Devs falling into the same trap of API’zation and doing over and over the same architectural error.
The Request Loop

Consider the following diagram:
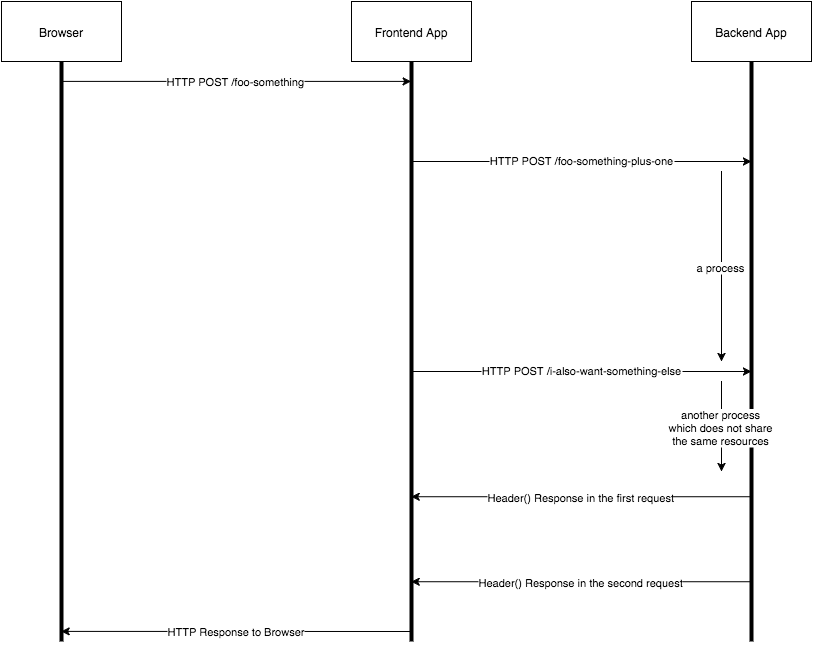
The Browser sends a request to the Frontend app. Now the Frontend App could forward it (or change it a bit) to the Backend App.
In our setup the backend app was a PHP app.
Now since PHP by default does not support threading (not pthreads), each HTTP request is a different PHP thread, served via apache.
This is very complicating, since you keep a connection (process) open and you open another one which could (at some point maybe) rely on data from the first one. You cannot access that data in between processes.
Not to mention that, you can not either debug this thing, since you insert a break point in the first request procedure, and the second request (which happens a few ms after) is being served without the debugging stopping at that point.
My point is that when you decide to go Microservice’d
Try to avoid request looping, when you need to do something that is synchronous. Or, use something different. Do threading. Use a message queue, or something else.
You will be surprised how much time you will spend trying to debug and understand what is wrong in this set-up.
I will close with the following meme:
Some people, when confronted with a problem, think, “I know, I’ll use threads,” and then two they hav erpoblesms.